With the installation of a good insulation of the ceiling in a residential building with a cold roof, heating costs are saved and heat loss is reduced. For this, heat-insulating construction products are used, different in type of manufacture and composition. It is important to know which heaters are most effective and how to properly insulate the attic floor to increase the building's heat efficiency.
The need for insulation for the ceiling
Insulation of the ceiling of the house allows you to raise the room temperature in the rooms, but condensation may appear in the attic. When warm air rises, it comes in contact with cold air, condensing moisture drops. As a result of this process, the insulating material is saturated with water and begins to actively rot with the formation of fungus and mold. In order to avoid such a phenomenon, it is necessary to change the physical conditions in the attic floor.

Concrete ceiling
Since concrete has a high coefficient of thermal conductivity, it consumes heat, but remains cold. As a result of this, condensation forms that can destroy the structure of the material during freezing. Therefore, the insulation of the attic flooring on a reinforced concrete slab occurs with the mandatory use of a vapor-permeable insulation to remove moisture out.
If there is no way to insulate the ceiling from the outside, then you will have to lay the material from the inside, but then it must be impermeable to steam in order to protect the concrete from moisture. A vapor barrier is also required for added protection.

Wood ceiling
Wood is susceptible to rot and various bacteria. With the incorrect organization of the thermal regime, the overlap will become wet and intensively collapse. In this case, the insulation of the wooden ceiling can be carried out both inside and out. With the external method, you can significantly save the space of the premises, and with the internal one, an impermeable quality material is required. It is also recommended that a vapor barrier be installed between the ceiling and the insulation for greater protection.
Varieties of vapor barrier
When warming the ceiling of a cold attic, the installation of a vapor barrier layer is an important process, because due to its absence the whole procedure will be inappropriate. After installing the insulation from the inside, the state of the ceiling will be unknown, and all sorts of effects on it will be hidden. In the future, this may be the reason for partial or complete restoration of the overlap. The most effective way to protect it is to install a vapor barrier.

Vapor barrier
It is an ordinary plastic film as an airtight barrier to wet steam. To save money, you can use a simple polyethylene sleeve, since it has the same properties as other polyethylene materials. Laying is carried out with strips of overlap of 15-20 cm and an inlet on wall structures up to 15 cm. Joints are necessarily glued with tape to achieve tightness.
When installing from the inside of the room, the film is laid only on top of an impermeable insulation, the same applies to installation on a concrete floor. If the insulation is carried out in the attic, then polyethylene is located between the wooden structure and the heat insulator.

Membrane
It is a film where only one side is permeable. It prevents the penetration of moisture, but does not prevent it from going outside. They are used to protect the insulating material from getting wet and sagging.
If the attic flooring is insulated on wooden beams with mineral wool, the vapor barrier membrane will provide free steam release, but it will protect the heater from external moisture, preserving its operational properties.

Features of cold roofs
To protect the residential building from the effects of external phenomena, a cold-type roof is arranged. There are many thermally insulating products that help reduce heat loss. The temperature inside and outside the attic should vary within 4 ° C, so the air through the ventilation ducts should go to the attic, and not into the space under the roof. Then the humidity and temperature indicators will correspond to the street. Otherwise, the imbalance of the regimes will lead to the destruction of the rafter structure and roofing.

The advantages of a cold roof are:
- Ease of maintenance. The roof has free space for access to any point, therefore repair and preventive measures are carried out without difficulty.
- Good waterproofing. A warm attic involves the use of add-ons that violate the integrity of the waterproofing material. When installing a cold roof, installation of additional elements is not required.
- Useful use. Despite the fact that the temperature in the attic is lower, it can be operated as a temporary warehouse, and later converted to an additional room.
- Minimum heat transfer surface area. Heat loss is only possible through the ceiling.

Inlet and outlet vents work as efficiently as possible at a great distance from each other. When they are installed under the wind board along the entire length, a full air exchange of the entire attic space is provided. Inlet openings are located in places of greatest pressure, due to which the blowing intensity increases.
A cold roof is arranged on various types of buildings with a height of 1-5 floors. Therefore, the installation of thermal insulation on the ceiling is calculated thickness depending on the material and the region of location (climatic conditions). Often it is laid in a layer of 20-50 cm. It is equally important to consider the exit sections of ventilation and chimneys through the attic floor. These zones contribute to the maximum removal of heat out.
Advantages of insulating the ceiling area
Roof insulation should be calculated at the stage of construction of the house. But often this question arises when the building is already finished, where thermal insulation was not provided earlier. When insulating a reinforced concrete or wooden ceiling in a house with a cold roof, you can get the following advantages:
- Maintaining a microclimate by preventing the penetration of heated air from the street in the summer season.
- In winter, it will protect the room from serious heat loss through the ceiling.
- The insulation additionally has soundproofing properties. Therefore, there will be no discomfort during heavy rain, wind or extraneous noise on the street.

Effective ways to warm the ceiling
There are several types of attic floor insulation: from the inside by nailing the insulation to the ceiling, and from the outside, using a rolled product and rolling it around the attic surface. Both methods are very practical, their main difference is the choice of the appropriate product and styling method.
Indoor work
When insulating from the inside, mineral wool can be used due to its high heat-insulating and vapor-permeable properties. Often, it fits inside a suspended structure of metal profiles and is sheathed with drywall. However, it is forbidden to compress, as it has air gaps. When compressed, they disappear, and thermal performance drops sharply.
Important! Despite its effectiveness, it is recommended to use mineral and basalt wool only for external insulation. Due to the low strength, microfibers are separated and, when ingested, cause side effects and serious diseases.
Other materials can also be installed on the frame or screwed directly to the ceiling, taking into account the laying of the vapor barrier layer.

Outdoor work
From the attic side, it is recommended to lay rolled or slab material, since it does not require careful fixing or manufacturing of the frame. This is a practical way, since the insulation does not select the useful height of the room. Before carrying out work, the surface should be well cleaned of foreign debris. Laying can be carried out in one or two layers with a thickness of 30-50 cm using mounting foam for fastening them.
If the attic space is not involved in the future, then additional coatings are not required. If it will be equipped for storing things, then the insulation is closed with a plank flooring or sheet moisture-proof plywood. When using bulk materials, coating is also not required, but this does not apply to dry leaves or sawdust.

Recommendations for thermal insulation work:
- thickness should be calculated according to the region of residence and the type of material,
- based on the selected products, you should know how to properly insulate the ceiling with a cold roof to ensure maximum effect,
- when laying several materials on top of each other, the vapor barrier performance should increase from lower to upper (on the contrary, it’s impossible),
- mineral wool should not be covered with expanded clay or vermiculite in order to avoid its punching,
- it is forbidden to lay a vapor barrier on both sides of the heat insulator so as not to trap moisture and not spoil the material,
- All joints of the connection of vapor and heat-insulating materials must be sealed to eliminate bridges of cold. To do this, use adhesive tapes, polyurethane foam, a special solution or glue.

Necessary tools
To carry out insulation work, you will need tools such as fasteners (screws, screws, dowels, anchors, liquid nails), building brackets, tape measure, a puncher for working with concrete, a screwdriver, a hammer, a construction knife for cutting sheet products.
The material is insulation, vapor barrier film or membrane, metal profiles to create the frame, wooden blocks 3x3 cm or 5x5 cm.
What insulation is better for the ceiling in a brick house
To effectively insulate the ceiling in a house with a cold roof, the following types of material are used outside and inside:
- Monolithic - has a high density and water resistance, while the dew point goes in any direction without compromising the properties of the insulation. These include extruded polystyrene foam.
- Fibrous or porous - made in the form of rolled material or mats. They are highly moisture saturated and lose their characteristics, therefore they are used only in conjunction with vapor barrier. Such types are distinguished: mineral wool, slab and sheet polyurethane foam.
- Bulk or sprayed - the first option is laid manually, and the second only with the help of special equipment.
From the outside, warming on the wooden beams of the attic floor is carried out using lightweight roll or bulk materials (sawdust, leaves). For concrete slabs, a solid monolith, slabs or heavy bulk material (expanded clay) can be laid.

Insulation for indoor use
Insulation of the ceiling in the premises is not recommended, however, in the absence of other options, this is possible. Since the house is warm and humid enough, the material can be exposed to mold and mildew.To avoid this, it is necessary to create a ventilation gap between it and the finish up to 3 cm thick, which will take even more room height.
The following products are used as insulation on the ceiling in a private house:
- Penofol - is a double material made of foil and foamed polyethylene. It is used in areas with a temperate climate, as it has average thermal insulation. It can be used as an independent layer, or combined with other types.
- Expanded polystyrene - practical for concrete floors. It is placed in a crate with a depth of about 3 cm and closed with finishing material (lining, drywall, Armstrong, suspended ceiling).
- Plaster mortars - they are characterized by high moisture resistance, fire resistance and decorative appearance. The mixture is used only for concrete substrates and includes thermal insulation components.
- Cork - cork material is moisture resistant, therefore it is used without vapor barrier. It is environmentally friendly, can serve not only as a heater, but also as a finishing material in a certain room design.
When choosing a heat insulator, attention should be paid to the material of manufacture of the floor and financial possibilities. It is recommended to insulate wood with dry products, and concrete slabs or cover with special compounds.

Methods of internal insulation of a cold attic floor
Before conducting external or internal insulation, it is necessary to calculate the thickness of the material according to the formula R = δ / λ, where:
- R - heat transfer resistance (according to the region of residence, for Moscow - 4.7 m² · ° C / W),
- δ is the thickness of the insulation layer,
- λ is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material (according to the normative document GOST).
Next, from the formula we find the thickness in this way: δ = λ · R.
Work begins with a thorough cleaning of the surface from debris, dust, cobwebs or moisture. When laying the product on the ceiling, be sure to leave a ventilation gap to protect it from mold and moisture buildup.

The use of penofol
Penofol consists of foamed polyethylene and a foil layer, it is used for buildings with a small level of heat loss due to low thermal insulation performance. To install insulation on the ceiling, you need to create a crate. The product is rolled over the surface of the frame and fixed with nails. The foil layer should look inside the room.
The creation of ventilation gaps on both sides provides for the presence of an additional crate, which is subsequently closed with sheet finishes or a stretch ceiling. The most effective use of penofol is possible in conjunction with penoplex to improve thermal insulation properties.

The use of foam inside
The material is practical for both external and internal use for thermal insulation of a ceiling with a cold roof. Warming is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The crate is made of a wooden beam with a thickness exceeding the thickness of the extruded polystyrene foam by 0.3-0.4 cm. The step between the rails is equal to the width of the insulation sheet with a residue of 1-2 mm.
- The material is installed in the cells, and with the correct assembly of the frame, the slabs must enter tightly with a little effort.
- The lath is closed with drywall, suspended or suspended ceiling.
Attention! To increase reliability, foam can be fixed to the ceiling using dowel nails of the “umbrella” type. A wide hat allows you to tightly press it without punching the fasteners.

Polyurethane foam and plaster mixes
Polyurethane foam refers to modern highly efficient products and allows you to create the perfect heat-insulating layer to reduce the heat transfer coefficient. The benefits when used on ceilings are:
- resistance to insects, bacteria,
- fire resistance
- high sound and waterproofing,
- high adhesive properties with various types of coatings,
- resistance to temperature differences.
Among the shortcomings, only complete vapor impermeability can be noted, which can serve as a violation of the microclimate in residential premises. Installation of a heat insulator is carried out with the participation of a specialist and the use of special equipment. It delivers the material in a thick viscous form under high pressure, filling all the cracks and covering the ceiling with an even layer. After drying, the layer thickness is about 10 cm.

Plaster mortars are less popular, but they have high thermal characteristics. Used for concrete substrates and have such advantages:
- decorative appearance
- environmental friendliness - does not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere,
- refractoriness - does not burn and does not spread flame,
- moisture resistance and mold resistance.
Cork material as insulation
White agglomerate is made from bark of cork. This type of natural origin is environmentally friendly, therefore it is widely used in any operating conditions, including as a heater. Often fit when creating a suspension system Armstrong with fixation in the cells of the crate. Agglomerate is resistant to moisture, therefore, does not require a vapor barrier layer.
Methods of external insulation of the attic floor in a house with a cold roof
To reduce heat loss in the room and save space, the installation of insulation can be carried out from the outside of the ceiling. This gives the advantage of using a greater number of different materials with high thermal insulation properties and low weight (does not create a large load on the supporting structures of the house).

Installation of plates and mats
The device of such options is carried out in one or two layers according to the following technology:
- Laying vapor barrier material. When installing a false ceiling, the membrane or film is nailed to the ceiling from the inside. If roll insulation is used, then the vapor barrier is laid on the side of the attic.
- Installation of a heat insulator. Products in the form of plates or rolls are stacked between the beams tightly without the formation of gaps. When using mineral or basalt wool this will not be a problem, and the gaps between the plates will have to be filled with mounting foam. It is better to choose products with a width slightly larger than the step between the beams, then the installation will go flawlessly.
- Gasket waterproofing. To protect the insulation from moisture, a waterproofing membrane is arranged with subsequent gluing of all the butt sections.
- Assembly of the counter-lattice. It is necessary to create a ventilation gap between the insulation and the plank flooring. The frame is stuffed on top of the beams to a height of 4 cm.

Application of sprayed materials
In this case, polyurethane foam or ecowool is used. They are applied to the surface with the help of special installations that ensure uniformity of the layer, dense filling of the space and high-quality thermal insulation.
Important! Using polyurethane foam, additional steam and waterproofing is not required. It is good enough to clean the surface of extraneous debris and blow out foam.
Ecowool can be laid manually with a uniform layer 10 cm thick, then compacted and sprinkled with a new one until a dense material of a given height is obtained. Such events are carried out quite rarely, since the effectiveness of special vehicles can reduce the time and labor required to complete the work. To prevent fibers from entering the room, the ceiling is protected by a vapor barrier film, and the insulation itself is waterproofed.

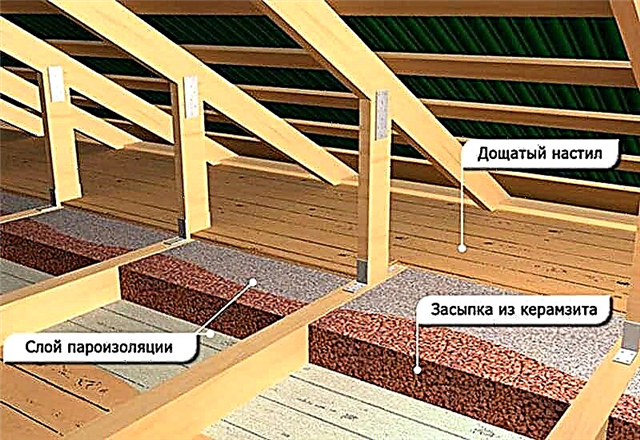
Bulk material laying
This type includes vermiculite, sawdust, expanded clay and wood leaves, although the latter option is used extremely rarely due to the fragility and increased hydrophilicity.Work on the installation of insulation for attic flooring is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Laying a vapor barrier (film or lap membrane).
- Mound of heat insulator. If expanded clay is used, then waterproofing is not required, since it repels moisture.
- Wind protection device. It is required to block the exit to warm air and protect against cold.
- Installation of flooring from boards with a thickness of 20-30 mm for convenient movement and storage of things.

Sawdust before use must undergo antiseptic and flame retardant treatment. When mixed with lime in a ratio of 5: 1, it is possible to protect the material from the attack of rodents. It is also recommended to make a solution of sawdust and cement in a ratio of 10: 1 and fill the ceiling with an even layer.
All technologies for laying thermal insulation material are practical and popular in modern construction. However, there are many other products of natural and artificial origin with thermal protection properties. The main selection criterion is the material of the building erection, since it is recommended to use the appropriate types of insulation for concrete and wooden houses.
Minvata
Mineral wool is rightfully considered one of the most common materials used to isolate heat loss through the ceiling. It is necessary to lay the insulation from the side of the residential or attic space, since its characteristics are perfectly combined with this type of work. 
This material is produced for isolation from different types of raw materials - it can be sand, glass break, blast furnace slag and even rock - basalt.
Slaggy
It should be noted that the insulation produced by processing blast furnace slag and called slag is not very suitable for thermal insulation of residential premises. The attic is an area with a high level of humidity, this is especially true for spring and autumn. Slag is notable for its high hygroscopicity, due to which its thermal insulation properties can be significantly reduced. The level of residual acidity of this insulator may not have the best effect on the building materials with which it is in contact. This is especially true for ferrous metals. 
Slag fibers are brittle and prickly, which is why it is not recommended to use it for decorating rooms intended for people. The smallest fragments of material can be suspended in the air and enter the respiratory tract. The main advantage of slagging is the price, which is much lower than other analogues.
Glass wool
Such insulation material is made from molten glass, drawn into the finest threads. From these wolves, panels of material are created that can be rolled up or cut into blocks. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of glass wool is lower than that of slag or basalt insulation. The moisture absorption index of this material is at the level of 0.55 ÷ 0.8 kg / m². 
Glass wool has been successfully used for the thermal insulation of ceilings on a cold porch. Often it is combined with other types of insulation. But it is worth considering that it must be laid strictly from the side of the attic, because, like slag, its fibers break easily and can negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes and skin membranes. Because of this, living quarters should be isolated from this type of insulation.
Basalt wool
Basalt insulation material is made from gabbro-basalt rocks and is considered the best choice for thermal insulation of the ceiling plane from the side of the room. Its fibers have greater plasticity in comparison with analogues, and therefore the degree of their fragility is lower. The material is sold in the form of durable mats made of tightly pressed fiber. It is little susceptible to the influence of the external environment, therefore it can be used for installation from the attic.You can also find insulation in rolls, the density of which is slightly lower than the slab version. 
Basalt wool is sometimes covered with a layer of foil. If the installation is done correctly, the insulation coefficient will be higher, since heat will be reflected inside the room. All varieties of mineral wool have one significant drawback. It consists in the fact that formaldehyde resins are used as a bundle of fibers, which are released into the environment and pose a danger to human health. Due to this feature, this type of insulator cannot be classified as an environmentally friendly type of raw material.
Expanded clay
Expanded materials include expanded clay, the raw material for the production of which is natural clay. It is perfect for thermal and noise insulation of the attic floor. The material does not burn and does not form harmful emissions when heated. The backfill layer may vary in density, since expanded clay is available in the form of granules of various sizes. Smaller grain size allows to obtain a higher density coating with high insulation performance. The optimal granular size of expanded clay for insulation of the ceiling is from 4 to 10 millimeters.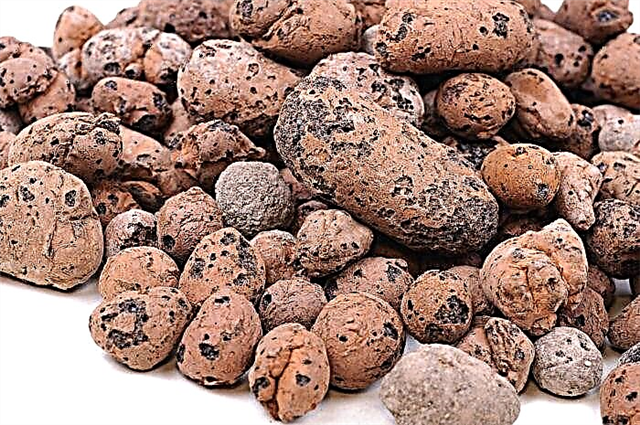 
Expanded clay is not dusty and safe for people with allergies. The operational life of the insulation is quite long, while the material retains its original quality indicators throughout the entire service life. The expanded clay is highly resistant to heat, it is often used to isolate a chimney from wood floors. The method is to backfill material into a metal box mounted around the pipe.
Ecowool
This type of insulation has not yet gained such high popularity as expanded polystyrene or mineral wool, but it is becoming increasingly used for insulation of walls and ceilings in a frame house. It consists of ecowool made of small cellulose fibers. The insulator can be laid “dry” or “wet”.
- The “dry” application method is carried out by scattering the material, which is then evenly distributed between the floor beams and compacted well.
- “Wet” installation is carried out using special equipment in which the insulator is connected to the adhesive composition and supplied outward under pressure.

The payback period with this method of insulation is from two to three years. It depends on the installation method and the thickness of the material.
Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene has been known as a heater for more than 50 years. During this time, it was possible to identify both the pros and cons of this material. Despite the shortcomings, it is still popular because it is quite cheap and easy to install. Expanded polystyrene is often used in combination with mounting foam, which serves as a means of sealing the insulation coating. The advantages of expanded polystyrene include a small indicator of thermal conductivity, which can fluctuate depending on the density and thickness of the insulation. 
The minuses of the material include a high degree of combustibility, while it melts and emits a lot of smoke containing toxins. Because of this, polystyrene foam is forbidden to be used in the construction industry in many European countries. It is replaced by extruded polystyrene foam, which is non-combustible and has the property of attenuating independently. Despite this, EPSP also refers to material with increased toxicity. Therefore, it is worth considering carefully whether it is worth giving preference to work on insulation of the home.
Polyurethane foam
This material is applied by spraying on an insulated surface, which is impossible without the use of special equipment. If necessary, polyurethane foam can be applied in several layers. Due to this quality, it is often used in thermal insulation of residential premises located in regions with severe winters.The applied material is able to fill all available gaps, as well as smooth out irregularities. The result is a sealed coating that has no seams. After solidification, it becomes so dense that it can withstand the weight of a person. The heat conductivity and water absorption are respectively 0.027 W / mK and 0.2%. This is evidence that the insulating qualities will not be lost even in high humidity conditions. 
When the material has hardened, any excess can be easily removed with a sharp knife. Thus, adjusting the polyurethane foam to the height of the floor surface is quite simple. Another plus of the polyurethane foam is that there is no need to equip the vapor and waterproof layers, since the material itself has the qualities necessary for this.
Sawdust
Small shavings and sawdust are one of the most inexpensive materials that have long and successfully been used for insulation of ceilings. Most often, wood processing materials are used in tandem - sawdust provides the necessary level of density, and shavings are responsible for the porosity of the coating. The popularity of such a heater is due to its low price and completely environmentally friendly natural composition, which they cannot boast of more modern materials. If the material is laid correctly, the ceiling will be properly insulated. But in order to achieve maximum performance from the material, an accurate calculation of the required layer thickness will be required. It will depend on the climate in the region of application. 
Lumber can be laid both in pure form or as part of a complex with other materials for insulation. Pallets that contain granules made from small compressed sawdust can be used. The main disadvantage of sawdust is their increased combustibility. Getting rid of this is not so difficult. It is enough to add flame retardants, clay or cement mortar to the composition before starting work. This processing method makes the material either non-combustible at all or slightly non-combustible.
When insulating the ceiling with sawdust, all wooden floor elements are pre-treated with flame retardants and insulated from the chimney. Electric wires are separated using special tubes with a corrugated surface.
Calculation of the amount of heat insulator
Our ancestors, living about a century ago, maintained heat in the home by erecting thick walls, up to 1 meter. Currently, there is no need to build such walls, because there is a wide selection of building materials on sale that can qualitatively protect the building from water and cold. They are quite dense and effectively reduce the level of thermal conductivity, and hence the heat loss. When preparing for finishing work, it is important not to forget about saving financial resources. For this, it is necessary before buying to correctly calculate the required amount of material for insulation, which will create a high-quality insulating layer.
General formula for calculating the required indicator
V is the volume of material in m3,
L - surface in m2.,
g is the thickness of the insulator in m
When calculating the specified indicators, it should be borne in mind that in 2009 the EnUV standard was officially adopted. It states that the minimum rate of heat loss by an insulating coating should be at least 0.24 W / m2hK. This value can be achieved by laying a layer of a heat insulator in the range from 13 to 40 centimeters. The layer thickness may vary depending on the selected material and its thermal conductivity. In addition, the type of construction is subject to accounting. In European countries, the requirements vary depending on how long the building was built - much more stringent requirements are imposed on new buildings than on buildings erected long ago.
Preparation work
The wooden surface needs careful preparation for the installation of insulation.
- The insulated surface is thoroughly cleaned of dirt and debris.
- All wood elements must be thoroughly coated with a flame retardant. The composition will increase the degree of fire protection. Pay particular attention to areas with gaps and cracks.
- It is necessary to get rid of signs of deformation and damage that exist on the surface. Large dents are filled with mounting foam, smaller ones are repaired with special putty for woodwork.

Preparation for the installation of insulation on a concrete surface is somewhat different:
- The ceiling is inspected for delamination of the decorative coating. Unstable places are cleaned, and then remove the formed dust and dirt.
- Existing cracks expand, get rid of dust residues, and then are treated with a sealing compound or putty.
- The final stage of preparation is the application of a deep penetration primer mixture.
DIY laying technology of the “pie” of thermal insulation
Laying of insulation material on the ceiling surface is made by one of the following schemes:
- Internal insulation - involves fixing the insulation on the surface of the wooden attic floor from the living area. Often, a drywall structure or suspended ceiling is subsequently mounted. Please note that this method of laying the insulator will reduce the total ceiling height by 10-20 centimeters. It is important to choose a heat insulator with a high degree of vapor permeability. This property is possessed by basalt and mineral wool, as well as penofol.
- External insulation - consists in the installation of insulation in the attic. This method is considered the most practical and profitable, since it does not require the arrangement of the final decoration, except in cases where a residential attic is equipped. For this method, such types of materials as expanded polystyrene, mineral wool, penoizol and expanded clay granules are most often used.

There are a number of reasons why the internal method of insulation is less preferred:
- The level of ceilings is noticeably reduced, which in a private house, and so may not be too large, and usually amounts to from 240 to 260 centimeters.
- There is no possibility of laying insulating material in bulk.
- The dew point shifts to the zone of internal overlap.
- You will have to dismantle the old ceiling coating and perform work on its refinishing.
With external insulation of the attic, the above drawbacks will be absent. But there are situations when there is no way to resort to the implementation of this method. Below are two options for installing a coating for thermal insulation of a home by insulating the ceiling.
List of required tools
To carry out insulation work on the attic, the following types of materials and tools will need to be prepared:
- insulation material itself
- wooden blocks or metal profile to create a lathing,
- hardware
- vapor barrier coating,
- building braces
- dowels,
- hammer drill

- hammer,
- screwdriver
- Roulette
- construction or office knife.
Inside mounting
Insulation works on the part of the dwelling are carried out when they are reconstructed in an old house, where the attic of the second floor is already equipped or access to it is impossible. Overlappings are isolated by one of the methods described below. The first of these involves fixing the material for thermal insulation directly to the ceiling. For this, a solution of special glue is used, plus additional fasteners with dowels. This method is optimal for reinforced concrete floors. 
The work algorithm is as follows:
- Priming the surface of the floor with deep penetration.
- Preparation of adhesive solution.
- Glue application on a fragment of a plate of material for insulation. The insulator piece treated in this way must be pressed as tightly as possible to the insulated surface and leveled to a horizontal level.
- After drying the adhesive solution (the process takes an average of 42 to 72 hours), its plates are additionally fixed with dowels with a large diameter cap.
- Drawing or fixing elements of the final finish of the ceiling.
Another method is to fasten the plates of the heat insulator to the equipped frame, consisting of a metal profile or wooden battens. The insulation itself is installed in the space of the cells of the lathing, after which it is fixed on the solid planks of direct suspensions, bent in a certain way. The method has proven itself in working with any type of overlap. Each of the options has a high degree of efficiency, despite the fact that the indicator of the thickness of the floor can be significantly limited in order to preserve the living space in the room as much as possible.
Installation from the outside
This method of thermal insulation of the ceiling is most preferred. This is due to the fact that the height of the ceiling does not suffer. In addition, the method allows not to violate the integrity of an existing repair, which significantly saves money, as well as labor and time for work. In this situation, it will be more preferable to arrange insulation on top of the ceiling. The installation of a heat barrier in this way allows you to use any type of material for this, including bulk ones. 
Consider the fact that the installation of ecological wool and sprayed polyurethane foam needs the involvement of specialists. And lay mineral wool, stick polystyrene and backfill expanded clay is possible on their own.
Finally
The process of warming the ceiling area is extremely important. Through the ceiling, up to 25% of the heat loss of the living room can occur. Work can be done both dry and wet. In the second case, a wet mass will be applied to the surface, which adheres the material to the base and also forms a soundproofing layer. 
The attic room is not protected from the street, except for the roof itself. This territory needs more than others warm insulation.
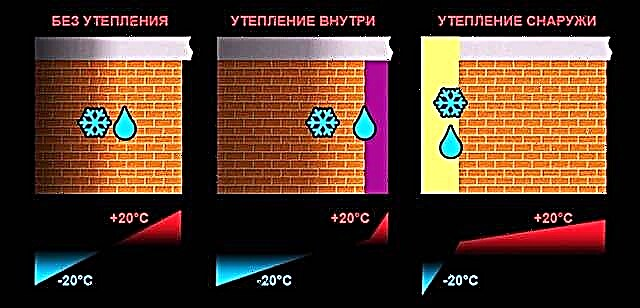
The eternal question is to insulate inside or out
Any external fence separating the living room from the street, it is better to sheathe the outside with thermal insulation. Accordingly, the ceiling insulation on the top floor of a private house is done from the attic. Causes:
- Installation is physically simplified, which is important when doing the work yourself. No need to make a suspended frame or hem the insulation from the bottom to the ceiling.
- An insulator layer 10–20 cm thick (depending on the region of residence) will not reduce the height of the rooms. This is an important plus for old buildings and "Khrushchev" with low ceilings.
- In an old house or apartment you don’t have to redo the repair.
- If you do not follow the technology of internal thermal insulation, the surface under the insulation will get wet, a fungus will appear. Condensation of moisture inside the "pie" contributes to 2 factors: the penetration of water vapor and the formation of dew points at the junction of dissimilar materials.
 When the outer guard is sewn inside, the moisture condensation point is located near the interface of 2 different building materials
When the outer guard is sewn inside, the moisture condensation point is located near the interface of 2 different building materialsAbout the notorious dew point that ordinary homeowners fear. To avoid condensation inside the structure, it is worthwhile to withstand 2 conditions: prevent water vapor from entering the room and use an insulator of sufficient thickness. Then the dew point will be inside the insulation, where there is nothing to condense. The second way is to organize the removal of moisture using ventilation (read below).
Reference. The dew point is a phenomenon of condensation of water vapor from air at a certain humidity and temperature. The lower the air temperature, the earlier the degree of extreme moisture saturation is achieved and condensation begins to precipitate.
There are exceptions to the rules, not every room can be finished with insulation from the outside. Examples:
- ceiling of the upper apartment of a multi-storey building,
- attic,
- balcony, loggia,
- concrete garage floor above the basement, cellar,
- the need for cost savings, etc.
 For obvious reasons, the garage basement cannot be insulated from above.
For obvious reasons, the garage basement cannot be insulated from above.In these cases, internal thermal insulation of the ceilings is arranged with strict adherence to technology. We will describe the work procedure in the form of step-by-step instructions, but first you need to find out ...
The better to insulate the ceilings
For insulation of ceiling structures, 4 groups of materials are used:
- Fibrous - mineral, stone (basalt) and glass wool.
- Loose - sawdust, clay, expanded clay, vermiculite.
- Polymers made of expanded polystyrene and polyethylene.
- Sprayed - ecowool, polyurethane foam, liquid foam - penoizol.
We will not focus on the last group of heaters - liquid mixtures are applied by spraying or filling cavities under pressure, which requires appropriate technological equipment. You cannot do such insulation of the ceiling in a private house with your own hands - you need to hire specialists from a specialized company and pay for services.
 Application of cellulose ecowool (left) and polyurethane foam PPU (right)
Application of cellulose ecowool (left) and polyurethane foam PPU (right)
Note. Spray materials are the most effective and expensive at the same time. Manually applied only insulating polyurethane foam Polynor with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity λ = 0.04 W / (m • ° C). The price of the aerosol can is 8 oz. e., the coating area is 1 m² with a thickness of 50 mm. Thermal resistance of the layer: R = 0.05 / 0.04 = 1.25 m² • ° C / W - the information is useful to us for comparison.
Let us consider in more detail each group of building materials, then we will choose suitable heat insulation materials for ceilings in various rooms.
Porous fiber materials
For the thermal insulation of roofs and attics under a cold roof, 3 types of fibrous products are used:
- mineral wool with a synthetic binder, thermal conductivity λ = 0.055-0.06 W / (m • ° С),
- non-combustible basalt heater λ = 0.05-0.053 W / (m • ° С),
- mineral wool based on fiberglass (otherwise - glass wool) λ = 0.044 W / (m • ° С).

Clarification. We provide insulation parameters for real operating conditions, taken from the normative building documentation. To overestimate the performance of insulators, manufacturers indicate the coefficient λ for the material in a dry state. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation resists cold.
Above, we calculated the thermal resistance R of penoizole 5 cm thick (1.25 m² • ° C / W). Let us compare the indicator with the characteristics of fibrous materials of a similar thickness by performing a short calculation for each (the method of SNiP is applied):
- minvata - R = 0.05 / 0.055 = 0.9 m² • ° C / W,
- stone wool - R = 0.05 / 0.05 = 1 m² • ° C / W,
- glass wool - R = 0.05 / 0.044 = 1.14 m² • ° C / W.
Output. In terms of thermal insulation properties, fibrous heaters lose to liquid and foamed polymers. Glass wool shows the best result, the worst - conventional mineral wool insulators. By the way, the values of thermal resistance R are interpreted the opposite: the higher the indicator, the more efficiently the insulation of a certain thickness works.
 Externally, basalt wool is different from the mineral color and corrugated fiber structure
Externally, basalt wool is different from the mineral color and corrugated fiber structure
We list the remaining, no less important properties of fibrous insulation:
- Cotton wool is produced in rolls, plates and mats of various densities - from 35 to 200 kg / m³.
- The open-pore structure contributes to good vapor permeability of materials.
- Mineral wool absorbs moisture, but with proper ventilation dries quickly.
- Basalt fiber is considered non-combustible because it can withstand temperatures of 600-700 ° C. Conventional mineral wool slabs also do not burn, but are destroyed by strong heating. Glass wool begins to melt at 250 degrees.
- Insulators do not have high strength, are attached to glue or using a frame.
Fiberglass-based cotton wool contains the smallest particles of glass, so it is not applicable inside residential premises. The well-known manufacturer of roofing insulation “Isover” recommends covering glass garret floors from the outside.
 Glass wool structure - fibers form many air spaces
Glass wool structure - fibers form many air spaces
Other mineral insulators use a synthetic binder containing formaldehydes. Under certain conditions, these substances can be released and mixed with air. With internal insulation, mineral wool should be well insulated from the living space with the help of a film, drywall and so on.
Loose heaters
All backfill materials are of natural origin, and therefore environmentally friendly. The following heaters go to the insulation of ceilings:
- expanded clay,
- fine chips, sawdust,
- clay,
- vermiculite gravel.
Reference. Vermiculite is much more expensive than expanded clay, so it is rarely used. Clay in its pure form is also not used - it is usually mixed with reeds or sawdust.
The main disadvantage of natural heaters is low efficiency in comparison with mineral and polymer products. Example: thermal conductivity of expanded clay gravel with a density of 200 kg / m³ is 0.11 W / (m • ° C). The heat resistance of the R layer of 50 mm will be only 0.05 / 0.11 = 0.45 m² • ° C / W. Indicators of expanded clay increased density, sawdust and clay even less.
 Vermiculite (left) and expanded clay gravel (right)
Vermiculite (left) and expanded clay gravel (right)
Briefly about the properties of building materials:
- All bulk heaters pass water vapor well.
- The combustibility of clay, expanded clay and vermiculite gravel is practically zero. Sawdust or reeds mixed with clay mortar also successfully resists fire.
- Long service life (excluding wood chips).
The low price of natural heaters is a relative concept. To create a heat-insulating layer comparable to mineral wool 5 cm thick, you need to fill in expanded clay to a height of 100 mm, that is, spend twice as much.
Characteristics of polymer insulation
To begin with, we give a list of materials used indicating the heat-conducting characteristics in operation:
- polystyrene with a density of 15 ... 35 kg / m³, λ = 0.045-0.041 W / (m • ° С),
- EPS extruded polystyrene, density - 20 ... 40 kg / m³, λ = 0.039-0.037 W / (m • ° С),
- foamed polyethylene 30 ... 50 kg / m³, λ = 0.044-0.042 W / (m • ° С).
Reference. Extruded polystyrene foam is often called Penoplex by the name of a popular brand. Products made of polyethylene foam are known by the names "Penofol", "Isolon" and "Tepofol".
For comparison with fibrous insulators, we determine the thermal resistance of polymers with a thickness of 50 mm:
- polystyrene 25 kg / m³ - R = 0.05 / 0.043 = 1.16 m² • ° C / W,
- "Penoplex" - R = 0.05 / 0.038 = 1.32 m² • ° C / W,
- “Penofol” - R = 0.05 / 0.042 = 1.19 m² • ° C / W.
It is noticeable that the thermal insulation performance of polymer insulation exceeds the characteristics of mineral and basalt wool. The leader is extruded polystyrene, whose result is comparable only with polyurethane foam applied by machine.
Other properties look like this:
- Thanks to the closed air pores, heaters practically do not let moisture through. An exception is foams having a meager vapor permeability of 0.05 mg / (m • h • Pa). The indicators of mineral wool are 0.4 ... 0.6 mg / (m • h • Pa).
- All polymers are flammable, no matter what sellers and manufacturers claim.
- Polystyrene-based materials are highly durable and are available in slabs.
- Foamed polyethylene has a soft and flexible structure, sold in rolls. To reflect the infrared heat flux, the insulation surface is covered with aluminum foil.

In terms of accessibility, polystyrene is in the lead - its price is comparable to natural materials. An “extruder” is sold at the price of basalt non-combustible cotton wool or even more expensive.
Useful fact. A good insulator can be a polymer stretch ceiling, forming an air gap under the ceiling. This cavity cannot be called hermetic, but there are very few paths for the penetration of warm air.
Selection tips
A review and comparison of the characteristics of insulation materials showed that each group of insulators has strengths and weaknesses that limit the scope of application. For example, flammable polymers cannot be used for insulation of floors on wooden houses — fire regulations prohibit it. You should not ignore the requirement - with the help of a heater, the fire will easily spread to the next floor.
Reference. When installing wooden ceilings, standards require that the supporting beams be treated with a refractory composition and non-combustible insulators are used. If you follow these instructions, then in case of fire, the ceiling will last 30-60 minutes until it collapses. Here is the answer to the question of whether it is possible to insulate a wooden ceiling with foam.
Based on experience in construction and other regulatory requirements, we will give the following recommendations for choosing thermal insulation:
- It is better to isolate wooden ceilings from the attic with basalt wool, expanded clay, vermiculite or a mixture of clay with sawdust.
- The ceilings in the rooms of the bath (especially steam rooms) need to be insulated with environmentally friendly materials. Here the choice is small - the same expanded clay, sawdust, vermiculite gravel, natural moss. No polymers and mineral wool, from strong heating, the release of harmful substances will begin.
- The ceilings of the attic rooms are sewn from the inside with dense basalt fiber, glass wool is not applicable.
- Concrete monolithic coatings are usually insulated with foam or polystyrene foam. In a country house - from the roof, on the balcony of a high-rise building or in the basement of the garage - from the inside.
- It is more correct to insulate flat reinforced concrete roofs with polymers from the outside, before the device of the surfaced bitumen roof. If this is not possible, Penoplex is hemmed from the bottom without problems, but with the observance of technology.
- Foiled foamed polyethylene is preferably used as an additional insulating layer. Find out how to properly insulate the ceiling with Izolon and Penofol from a separate manual.
Practice shows that it is better not to combine wood and vapor-proof building materials. The polymer, which is tightly adjacent to the beam, blocks the access of air; wood does not “breathe”. If steam begins to condense at the junction and has nowhere to leave, the tree will turn black and rot.
How to calculate the thickness of thermal insulation
The determination of the thickness of the insulation layer will be shown by examples. As a basis, we take the formula for calculating thermal resistance (in the previous sections we already used it to compare the effectiveness of different materials):

- R - heat transfer resistance of the insulating “pie”, m² • ° C / W,
- δ is the thickness of the insulation, m,
- λ is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material, W / (m • ° C).
The essence of the calculation: according to the standard thermal resistance set for your region of residence, calculate the thickness of the insulation, knowing the characteristic λ. The value of R is determined according to the scheme given in the regulatory documents, a map with indicators for the Russian Federation is shown in the photo.
 Similar cards can be found in regulatory documents of other CIS countries.
Similar cards can be found in regulatory documents of other CIS countries.
Example 1 It is necessary to calculate the warming of the cottage with an attic located in the suburbs. We find the R characteristics for Moscow, choose the indicator 4.7 m² • ° C / W (for coatings), take the coefficient λ of basalt wool equal to 0.05 W / (m • ° C) and calculate the thickness: δ = 4.7 x 0.05 = 0.235 m ≈ 240 mm .
Example 2 We determine the thickness of the insulation layer from "Penoplex" for concrete floors, location - Cherepovets. The algorithm is as follows:
- We find on the Internet or reference literature the thermal conductivity of reinforced concrete λ = 2.04 W / (m • ° C) and find out the thermal stability of a standard slab 220 mm: R = 0.22 / 2.04 = 0.1 m² • ° C / W.
- According to the map, we find the standard value of R for Cherepovets, we take the overlap index - 4.26 m² • ° C / W (the figure is highlighted in green).
- Subtract the required resistance of the plate from the required heat transfer value: 4.26 - 0.1 = 4.16 m² • ° C / W.
- We calculate the thickness of polystyrene foam insulation λ = 0.037 W / (m • ° C): δ = 4.16 x 0.037 = 0.154 m ≈ 160 mm.

Comment. The algorithm does not take into account the heat resistance of the interior decoration and attic floors, therefore it gives a result with a small margin. If we take away the resistance of the flooring boards and gypsum plasterboard hemming, the thickness of the EPSF will decrease to 135 mm.
We warm mineral wool flooring
As already mentioned above, mineral wool is used for insulation of wooden ceilings and ceilings of attic rooms. So that the material is not saturated with moisture and does not lose heat resistance, it is necessary to withstand 3 conditions:
- protect cotton wool from water vapor from inside the premises,
- provide ventilation of the outer surface, so that the resulting moisture is eroded from the thickness of the insulation,
- the vapor permeability of the materials used in the “pie” should increase towards a colder room or street, as shown in the diagram.

Plate or roll mineral wool is located in the space between the ceiling beams, as shown in the insulation scheme. When installing thermal insulation with your own hands, observe the following procedure:
- Roll out a vapor barrier film from the bottom of the beams, laying adjacent sheets with an overlap of 100 mm wide. Lap onto walls 10-15 cm wide. Carefully glue joints with tape.
 The right photo shows the option of waterproofing with foamed polyethylene with a reflective layer of foil
The right photo shows the option of waterproofing with foamed polyethylene with a reflective layer of foil



An important point. Between the surface of the cotton wool and the waterproofing, a ventilation duct is necessarily provided. Thanks to the air gap, moisture is removed from the insulation.
Sometimes builders lay the first waterproofing film over the boards of the draft ceiling, bypassing each beam. We do not recommend using this approach - vapor barrier will close the air access to the log wood, and from below it will remain open for steam saturation. Further it is clear - the tree will rot.
How to lay mineral wool on the ceiling, if the thickness of one layer is not enough. In such cases, a second tier of heat-insulating plates, shifted by 30-50 cm relative to the first row, is made. If the height of the load-bearing beams is not enough to organize the air, the frame of the battens of the crates is built up, then a second layer of insulation and waterproofing are arranged.
 The left side shows the additional crate device when the height of the beams is not enough
The left side shows the additional crate device when the height of the beams is not enough
The attic cover insulation scheme is very similar to the thermal insulation of a wooden floor:
- A counter-lattice is provided on the roof, the diffusion membrane is rolled from above along the rafters. If there is no external frame, the waterproofing can be fixed from the inside, bypassing each rafter leg and shooting the edges of the paintings with a stapler.
- The insulation is placed between the rafters at a loss. If the width allows, we put the plates in 2 layers with a dressing, otherwise we mount a horizontal counter-lattice.
- We beat the vapor barrier to the rafters through the rails, to which the interior finish of the gypsum board or lining is subsequently attached.

Reminder. When working with glass wool or basalt fiber, do not forget to wear a respirator and gloves, the material is very dusty and irritates the skin. How to isolate a wooden coating without errors, look at the video:
Two options for thermal insulation of ceilings
The ceiling is insulated if a non-residential attic is located above it, respectively, not equipped with thermal insulation.
It is not used as a living space in winter; therefore, it does not need to be laid on a slope. Often this is just a warehouse for inventory and a room for drying mushrooms / berries.

The non-residential attic itself plays the role of an air chamber that impedes the movement of thermal waves both inside the building and out. However, to dry the wooden elements of the frame structure, roofing, metal fasteners, the cold attic is usually equipped with effective ventilation.
Ventilate it naturally, i.e. regular airing without using any mechanisms. The system operates without coercion. Air moves due to the difference in temperature with pressure outside and inside the attic.
Airflow enters the attic through the dormers in the summer and the gaps framing them in the winter when a vacuum forms inside. It is removed spontaneously, driven out by a new portion coming from the street.

For building structures, constant air circulation is really necessary. But along with continuously moving air masses, heat is blown out of the attic. As a result, instead of saving it to save energy, additional costs are obtained.
How to deal with them? Be sure to insulate! Warming is done in two standard ways, these are:
- Thermal insulation device on the ceiling on top. Those. from the attic, on the reinforced concrete floor or between the wooden lags, they lay foam polymer slabs, mineral wool, add expanded clay or folk remedies (sawdust, dry foliage, etc.).
- Installation of stove insulation from inside the premises. Simply put, the mounting of polystyrene plates from the premises to the lower plane of the ceiling.
In both cases, the insulation layer increases along the perimeter, i.e. along the line joining the floor and adjacent wall. Strengthening is required due to increased heat loss. A vapor barrier membrane is located between the wall, the ceiling and the insulation layer.

Why is non-waterproofing used in the formation of a heat-insulating pie over the overlap? Yes, because it is necessary to protect it, first of all, from steam penetrating from residential premises, and not from atmospheric water flowing from above.
It is the vapors released during breathing by us, our pets and domestic plants formed during the preparation of food that, during the intake of hygiene procedures, can harm the thermal insulation system. But on top of the water must protect the roof.
By the way, when laying all types of insulation from the side of a cold attic, they are not blocked from above by either steam or waterproofing. This leaves the opportunity for materials to dry out spontaneously when ventilating the attic space.

In no case should “rub” and “get wet” under practically sealed insulation film to heaters. Together with moisture, they lose their insulating properties. Wet thermal insulation saves almost nothing, but it can rot, and the mold spreads to the wooden elements.
The vapor barrier under the insulation, laid on the side of the attic, is arranged in the form of a trough: with the edges of the panel coming onto the walls. So it will prevent the insulation from getting wet not only from steam moving upward from the side of the premises, but also from the side of the walls that absorb atmospheric moisture.
Do not use a vapor barrier layer only if extruded polystyrene boards are used as thermal insulation. They have virtually no pores that can absorb and retain moisture.
Moreover, this is allowed exclusively over rooms with a stable "dry" operating mode. Over the bathrooms, showers, pools, the vapor barrier layer is paired with extruded polystyrene as usual. After all, there is the possibility of moisture penetration between the joints of the plates.

Insulation from the attic
Almost all types of insulation materials are used in the insulation of the ceiling from the cold attic. Bulk options, rigid foam slabs, soft cotton mats are in use.
Both products manufactured by industry and good old folk materials are used. The main advantages of the former include manufacturability. Their manufacturers thought through and provided everything for the operational implementation of lightweight styling.

Folk remedies to lay much harder. They are not easy to collect in the required volume, and even delivered to the place of work, which is most often done manually in buckets. But they are much cheaper, better than industrial products coexist with wood and do not emit toxins harmful to us.
Thermal insulation from the attic space involves periodic maintenance of the insulation system.
Bulk materials need to be loosened periodically so that they are better dried, the rest inspected and artificially dried, for example, with a hairdryer if necessary.
For inspection and maintenance of the lags above the thermal insulation, “paths” are constructed from two or three boards. If it is supposed to fill the screed on heat-insulating plates and hard mats, then the trajectory of the proposed path is laid out with a reinforcing mesh.

Use of mineral wool
Mineral wool group includes glass wool, stone (i.e. basalt) cotton wool and slag wool. In recent years, glass wool has been used less and less because of its ability to abundantly “dust” with small glassy particles, which are strictly forbidden to inhale.
Work with glass wool is permitted only with a respirator and glasses. In addition, the smallest glass fibers are harmful to the skin.
Therefore, to personal protective equipment should be added jumpsuit made of dense fabric with durable elastic bands on the legs and sleeves, and even gloves.
Slag for insulation of ceilings in low-rise buildings is not used due to toxicity. There remains basalt, it is also stone wool, produced from volcanic rocks. This is because it is not harmful to operate and easy to install.

The technology of thermal insulation with basalt wool is determined by the type of overlap:
- On reinforced concrete floors. First, the base is repaired and leveled, then the vapor barrier is laid with the edges on the walls. After the mats are rolled out and laid in 2 layers so that the butt seams of the lower tier overlap with the middle of the upper mat, i.e. apart.
- On wooden floors. Mats are laid in the space between the lags. Previously, vapor barrier material is placed in each “cell” formed by the lags with access to the logs and along the perimeter on the walls.
Cotton wool before laying cut. Cut it so that the piece is at least 2 cm wider and longer than the actual cell size.
Before reinstalling, the cotton piece is slightly squeezed so that after it straightens out in the right place and covers the entire space with it. So exclude the formation of cold bridges.

Thermal insulation with polystyrene plates
Plate heaters are mainly used for reinforced concrete floors. For laying in the space between the lags it is difficult to choose the size.It is necessary to cut, lose time, and often material when illiterate cutting, and in general it is difficult to do everything without gaps, and these are ways for heat loss.
In the arrangement of the insulation complex on reinforced concrete floors, two types of plate thermal insulation are used:
- Styrofoam. He is non-extruded polystyrene foam. The material requires the mandatory installation of a vapor barrier layer before laying due to the fact that there are channels in its structure that can absorb water.
- Extruded Polystyrene. Most often it is Penoplex. Thanks to the practically waterproof surface, before laying it above living quarters, bedrooms, living rooms, children’s rooms, it is not necessary to lay vapor barrier.
Before installing the thermal insulation from the side of the cold attic, the bases must be repaired and leveled. The vapor barrier film is laid in the form of a pallet with sides curved onto the walls.

Stack plates freely. They are placed in two layers with a spacing of seams in the lower and upper tiers. If Penoplex with a mounting chamfer is used, the seams do not need to be sealed; if the foam is plastic, then the seams and stacks are filled with sealant or polyurethane foam.
The screed on the plates is most often performed partially, only at the location of the service tracks. It is either poured with a cement-sand mixture with a reinforcing mesh with a layer not exceeding 4 cm, or constructed of gypsum-fiber sheets.
If filled with a solution, then waterproofing is laid on the insulation. Purely so that the concrete milk does not leak into the insulation and does not affect its insulating qualities.

Expanded clay gravel
The most famous backfill insulation material is expanded clay. It is used directly for warming, and to facilitate insulating compounds and mixtures. Expanded clay is produced in the form of gravel ranging in size from 4 to 10 mm.
Expanded clay is made from environmentally friendly easily sintered clay. The material is affordable, non-combustible, moisture-proof, lightweight, which greatly facilitates delivery and backfilling. They fill it either into the space between the lags, or directly onto the reinforced concrete floor.
Before filling expanded clay, the base is covered with a vapor barrier film, the edges of which traditionally go to the walls. These peculiar sides should be 10-15 cm above the level of the layer of gravel poured on the ceiling.

Expanded clay service tracks are optional. You can walk right on the backfill. Periodically, it is necessary to stir a rake in order to dry all the artificial pebbles of the insulation layer.
In addition to expanded clay, an extensive range of popular zapy means of insulation is still being used, attracting mainly owners of eco-houses as adherents of materials safe for themselves and the environment.
Bulk Folk Materials
Adherents of environmentally friendly construction methods have their own opinion, based on centuries-old successful practice, regarding the options for thermal insulation of the ceiling.
They believe that insulating both directly the ceiling under a cold roof and ramps correctly and reasonably with natural materials.
In terms of insulating qualities, natural options are certainly inferior to heaters of industrial production.

But thermal insulation of natural origin is distinguished by:
- Environmental priorities. They do not pose the slightest threat to the environment, do not emit and do not spread harmful chemical components. Natural heat insulators do not need to be disposed of in a special way, they can simply be burned or put in a compost heap.
- Practicality. Folk heaters perfectly retained heat even in those days when the house was heated only by a stove. In addition, there was no such powerful heating equipment that the current owners of private houses have.
- Economic advantages. Natural insulation can be prepared for a penny or generally free of charge.Replace with the loss of technical characteristics can be much more often than factory products.
- Symbiosis with natural building materials. Natural heat insulators are excellently adjacent to wood, clay, soil backfill. Under stable temperature conditions, they do not deteriorate from contact with the stone.
- Safety for residents. In extremely rare cases, natural materials can cause an allergic reaction, the origin of which is undeniable chemical prerequisites.
Most natural heat insulators according to the method of laying belong to the backfill varieties. They are freely distributed over the ceiling, periodically ted to dry and increase thermal insulation properties. For service, arrange tracks from a pair of boards laid on logs.
One of the popular options for natural insulation is ecowool made from natural cellulose. Its advantages include manufacturability of application, thoroughly thought out by manufacturers, and the implementation of pre-treatment with flame retardants and antiseptics.

To this day, as a natural thermal insulation:
- Shavings and sawdust. Their abundant number remains after the construction of a wooden house, you can replenish supplies at sawmills and in woodworking workshops. Fall asleep with a layer of 15 - 30 cm.
- Straw. You can harvest it at the nearest cereal farming farm. Stacked in a layer of 25 cm.
- Moss. Magnificent, practically non-decaying thermal insulation, used both inside the building and outside. The qualities laid down by nature allow the use of moss for ten years or more. The insulation layer can be relatively insignificant, up to 10 cm.
- Dry foliage, hay. It is possible to stock up with such thermal insulation absolutely free of charge, but will have to be changed almost annually due to the tendency to quickly saturate with moisture. You can use not only foliage, but also needles. It is enough to insulate with a layer up to 20 cm.
- Seaweed. Not all regions of our country can freely get this option of insulation. True, the inhabitants of Primorye have plenty of them and can change every year. The styling power is up to 20 cm. Distribution of volatile iodine molecules that are useful for people is considered a significant advantage.
If your area has a pond overgrown with reeds, this plant will also serve. Its stems are connected together by a bundle or metal wire. Then, bundles fill the space between the ceiling beams and lags.

The above types of natural thermal insulation have a number of significant disadvantages that are not characteristic of factory products. Therefore, to increase consumer qualities, backfill natural heaters must be carefully prepared before installation.
The disadvantages that should be minimized before use, quite rightly include:
- Flammability and ability to maintain excellent combustion. Flame retardant is ideally combating this drawback. Instead, you can use clay or slag, a layer of which is closed on top of the insulating backfill.
- Thermal insulation reduction. The heat-insulating natural bookmark must often be ted up to avoid pressing, it must be dried to prevent wetting and a decrease in the insulating properties associated with it.
- Incoherence. During the maintenance of the insulation and the device within the attic of the drafts necessary for drying, part of the material can be trivially taken out. So, you need to constantly replenish the stock. This disadvantage can be overcome by laying in bales.
- Rotting tendency. The ability to quickly and easily absorb moisture can lead to decay, especially if regular maintenance is neglected. As a prophylactic, antiseptics used for treating wood are suitable.
- Attraction for rodents. In dry and warm bookmarks made of straw, moss, hay, rats and mice live freely, for the frightening of which they will have to purchase specialized products in the SES.
There are two more popular varieties of folk thermal insulation, this is the soil and plant layer and crushed clay. They do not burn or attract mice.
They are not afraid of moisture and drafts weathered dry plants. But there is a serious drawback - considerable weight, because of which it is necessary to strengthen the overlap.

Soil - a soil layer in contact with the day surface, enriched with the products of vital activity of representatives of flora and fauna, to facilitate mixing with any of the abovementioned folk heat insulators. It is simply scattered over the ceiling, like expanded clay.
Clay is diluted in a container with water to the consistency of sour cream, added to it, cut straw or shavings, and poured onto the overlap with a layer of 10 - 15 cm. After the solidified composition has hardened, the cracks are closed with softened clay.
Thermal insulation technology
If, for technical reasons, insulation from the cold attic is not possible, then the insulation systems are installed from the side of the room, i.e. put on the ceiling. This option is more difficult to implement, but sometimes it is the only possible one.

In the case of floor insulation from the ceiling, the following are used:
- Styrofoam. Unextruded expanded polystyrene panels are simply glued onto a pre-aligned ceiling. A silicone sealant or a mounting foam is introduced into the gaps between the elements, the excess of which should be removed immediately.
- Extruded polystyrene foam. Also stick. Most often, Penoplex is used with a mounting edge that eliminates the likelihood of cold bridges. The thickness of the insulation can be accurately calculated according to the climatic data of the area and select the material with the appropriate characteristics.
- Bung. The simplest option is a cork sheet substrate used as a flooring for underfloor heating. Panels glued to the ceiling are also suitable, but the cost of the insulation system as a result will be much more expensive.
Gluing while holding the canopy material is, of course, much harder and harder than falling asleep on top. In addition, these options are not applicable without external decoration. They just need to be decorated.
Masking of the ceiling insulation system is carried out by installing frame structures: stretch and rack ceilings. For their installation, a fixing profile is installed around the perimeter of the room, located at least 1-2 cm below the glued insulation.
If you plan to install ceiling lights and exhaust ventilation ducts, the distance between the plane of the decorative ceiling and the thermal insulation system is still increasing. As a result, it may turn out to be too low, as it were, a “pressing” ceiling, which negatively affects the interior picture and the well-being of the owners of the house.

Variants that are actively used in practice include one- and multi-level drywall constructions. Rigid GVL option is a priority due to the fact that in case of wetting and peeling off the heat-insulating plate, it will freely hold the detached part.
In the field of building a thermal insulation system from the inside, heat-insulating plasters stand apart. Materials for their implementation have developed relatively recently. The pioneers in their application were progressive industries: the military-space complex, civil aircraft industry.
As part of the heat-insulating plaster material applied to the ceiling, there are tiny ceramic balls inside which air is contained. He is the most active insulator.
A valuable advantage of heat-insulating plasters is the ability to apply the thinnest layer of 1 mm, the effectiveness of which will be equal to the effectiveness of a foam plastic plate with a thickness of 5 cm. Minus is the considerable cost and complexity of the application, which requires special equipment.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1. Correction of errors in the device of thermal insulation of the ceiling made by the former owner of the house:
Demonstration of the process of warming the attic with mineral wool:
The use of ecowool in the thermal insulation of the ceiling:
Properly executed thermal insulation of the ceiling will ensure perfect heat preservation, while creating the conditions for unhindered removal of household fumes and condensate outside the roof structure.
However, not only technologically precisely performed work is important, but also the correct selection of the insulation scheme and material for its execution. We hope that our article will provide you with effective assistance in this matter.
Features of the device of cold roofs
The design of the roof depends on the nature of the use of the house and the roof space. The choice of form, roofing material, the scheme of the roof frame and the presence or absence of a thermal insulation layer depend on these factors. In private housing construction, 2 types of roofs are used:
- Warm roof. This type of roofing construction provides for complete insulation of slopes. A warm roof is mounted if the room located under the ramps is used as a residential one. It is considered an excellent option for equipping a residential attic. It makes sense to build roofs of this type for houses used and heated all year round, since they exclude heat loss through slopes. The cost of materials and installation work on the construction of a warm roof is much higher than the cost of building a cold one.



Important! If the attic is not heated, then the air in it serves as a kind of buffer zone, which performs the function of thermal insulation and reduces heat loss. The air rising from the heated rooms of the first floor according to the law of convection is gradually cooled and does not heat the surface of the slopes from the inside, so that ice does not form on them.
To keep heat, as well as reduce fuel consumption to maintain optimal temperature, heat insulated ceiling located under a cold roof using heat-insulating or fibrous thermal insulation materials. Since heated air always rises, this operation is an effective measure to reduce heat loss.
Thermal insulation methods
High-quality thermal insulation reduces heat loss and heating costs by 30%, which is a good saving on the scale of the family budget. Using a suitable insulation and the right choice of installation method form a comfortable microclimate in the room.
The issue of thermal insulation of a ceiling under a cold roof is best solved at the stage of building a house, then you can choose the most effective and convenient option. Most often, the insulation is mounted in 2 ways:
- Insulation from the attic. The builders consider the most effective and correct insulation of the ceiling, located under the cold roof from the attic. The fact is, the ceiling is most often constructed of wood, which in itself is a good peat-insulating material. In this case, the insulation is laid on the attic floor and closed with a draft floor. If the insulation is carried out from the attic side, then materials in the form of plates or filling can be used.

Insulation from the ground floor. In cases where there is no access to the attic, when reconstruction of old houses with a ready attic is carried out, thermal insulation is performed from the side of the first floor.For this, a frame of metal profile or wooden battens is mounted on the ceiling, insulation plates are laid there, and then sheathed with drywall. The disadvantage of this method is that it reduces the height of the ceiling. In addition, mounting at the top is always much more difficult and longer. The effectiveness of this method of insulation is less, so it is used when there is no other way to reduce heat loss without dismantling the floors.

Note! Any thermal insulation works comprehensively. Therefore, if you want to solve problems with heat loss in a house with a cold roof, do not forget about the thermal insulation of the floor, door and window openings. An obvious way to analyze where the heat goes is to look at the house in the thermal imager in winter. To increase the energy efficiency of the house, you need to pay attention to the areas painted in red and yellow, it is through them that the heat leaves.

Materials
The modern construction market offers an impressive range of materials for thermal insulation, but not all of them are suitable for warming the ceiling under a cold roof. In order for the costs to recover, it is necessary that the thermally insulating layer be resistant to moisture, have low thermal conductivity and meet safety standards for human health.
For insulation use the following materials:
- Expanded clay. Expanded clay is called a backfill insulation, which is obtained by burning shale. It has a light weight, porous structure and high heat-insulating properties, but is not afraid of moisture. To insulate the ceiling with this material, a vapor barrier film is laid on the attic floor, fixed with a construction stapler, and then expanded clay is covered with a layer of 15-30 cm.If the finishing floor is installed in the attic, then the space between the lags is filled with insulation.
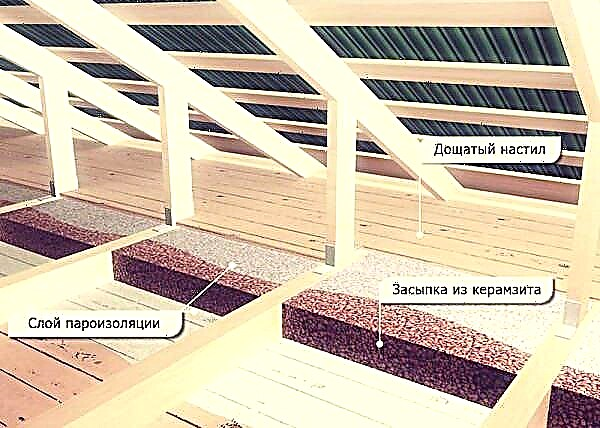


Experienced craftsmen remind that vapor barrier and waterproofing layers play an important role in warming a floor located under a cold roof. To protect the insulation from getting wet as a result of interaction with heated air saturated with water vapor, a vapor barrier membrane is first laid. And from the roof side it is protected from leaks with a waterproofing film.







